Introduction: Diving Deeper into Neuropathy Types
Neuropathy doesn’t come in a one-size-fits-all package. It’s a complex condition characterized by damage to one or more nerves, which manifests in various forms depending on the nerves affected. This blog dives into the three primary types of neuropathy: sensory, motor, and autonomic, each affecting different functions of the body and requiring unique management strategies.
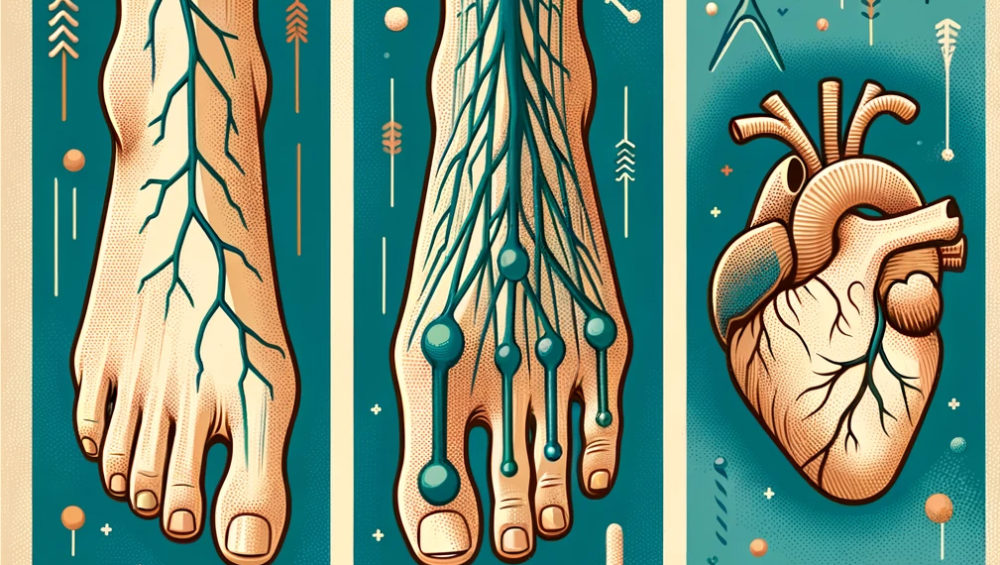
Understanding Sensory Neuropathy
Sensory neuropathy occurs when nerves that carry messages of touch, temperature, pain, and other sensations to the brain are damaged. This type of neuropathy is perhaps the most familiar due to its common symptoms, which include:
- Pain and Tingling: Often described as a burning, tingling, or prickly sensation.
- Numbness: Especially in the extremities, potentially leading to balance problems.
- Hyper-sensitivity: An increased sensitivity to touch, where even light contact can feel uncomfortable.
People with sensory neuropathy may find it difficult to walk or perform tasks that require fine motor skills due to the loss of positional awareness of their feet and hands.
Exploring Motor Neuropathy
Motor neuropathy affects the nerves that control muscle movement. When these nerves are damaged, it can lead to:
- Muscle Weakness: Making it hard to climb stairs or lift objects.
- Muscle Atrophy: Where muscles shrink in size.
- Cramps and Twitches: Often disturbing and painful.
This type of neuropathy can severely impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities, leading to reduced independence.
Autonomic Neuropathy: The Invisible Impact
Autonomic neuropathy involves the nerves that control the body’s automatic functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure regulation. Symptoms can be wide-ranging and sometimes dangerous:
- Digestive Issues: Such as constipation, uncontrolled diarrhea, or gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying).
- Cardiovascular Issues: Including abnormal heart rate, blood pressure fluctuations, and issues regulating body temperature.
- Urinary Problems: Such as incontinence or difficulty urinating.
Because the autonomic nerves cover such a broad range of functions, this type of neuropathy can be particularly challenging to diagnose and manage.
Conclusion: Addressing the Challenge
Understanding the type of neuropathy is crucial for effective management. Each type affects the body differently, and recognizing the specific symptoms can lead to better-targeted treatments and improved quality of life. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to seek medical advice to get a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.